Session Manager¶
It is possible to configure the Session Manager to manage execution environments at an enterprise level. This feature is especially useful for companies with multiple Runners that want to automatically and efficiently distribute automation tasks among different hosts.
Context¶
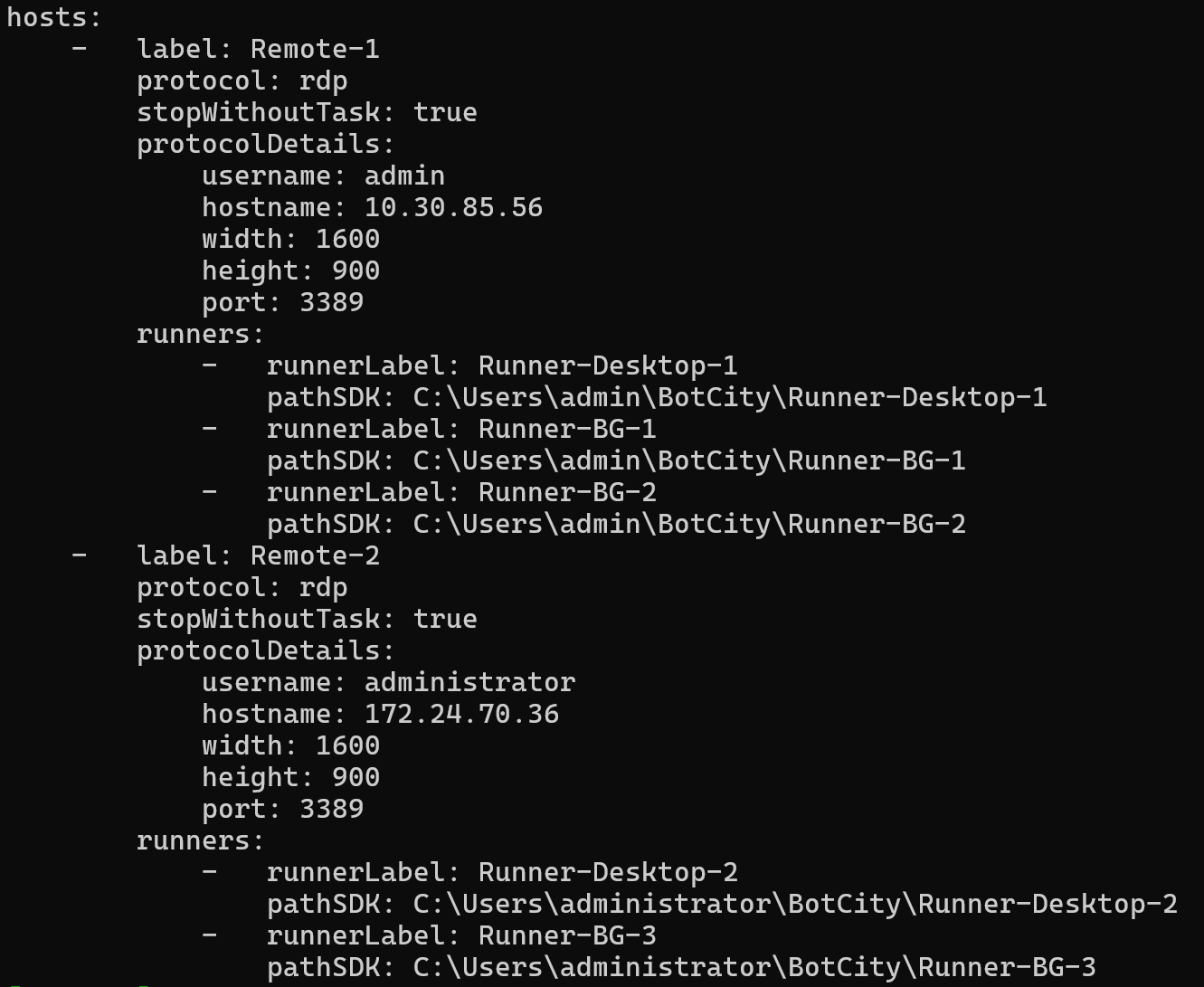
A company with 5 Runners in the BotCity Orchestrator can distribute them in various ways.
Suppose the company has two remote machines (hosts) for running its automations. The distribution can be as follows:
- First Host:
Remote-1- Associated Runners:
Runner-Desktop-1Runner-BG-1Runner-BG-2
- Associated Runners:
- Second Host:
Remote-2- Associated Runners:
Runner-Desktop-2Runner-BG-3
- Associated Runners:
Each host has a set of associated Runners responsible for executing automation tasks, with only one Runner controlling the screen per machine and the rest running background processes to avoid interfering with screen manipulations.
The Session Manager is the component that manages the allocation of these tasks among the available Runners on the hosts.
Session Manager¶
The Session Manager can be allocated on a dedicated machine or a user machine. The important thing is that this machine is available to constantly monitor the BotCity Orchestrator task queue, since the trigger for managing the hosts is a new task created in the queue.
The machine must also be able to reach the hosts where the Runners are installed via RDP and have communication enabled with the BotCity Orchestrator via HTTPS (Port 443).
Environment configuration suggestion
For an environment dedicated only to running the Session Manager:
- OS: Linux
- RAM: 2GB
Pay attention to possible requirements regarding network communication or other resources you wish to add.
Session Manager Configuration¶
Based on the context above, let's configure the Session Manager to manage the Runners associated with the hosts.
Step 1: Download Session Manager¶
Session Manager is part of the BotCity SDK and can be downloaded directly from the Orchestrator by selecting the desired operating system. This example uses Windows, but the process is similar for other operating systems.
Download
For more details on how to download and install the SDK, see the full documentation at BotCity SDK Installation.
Step 2: Access Session Manager¶
After installation, Session Manager will be available among the BotCity SDK tools.
In the terminal, navigate to the installation folder and use the command to check the visibility of Session Manager:
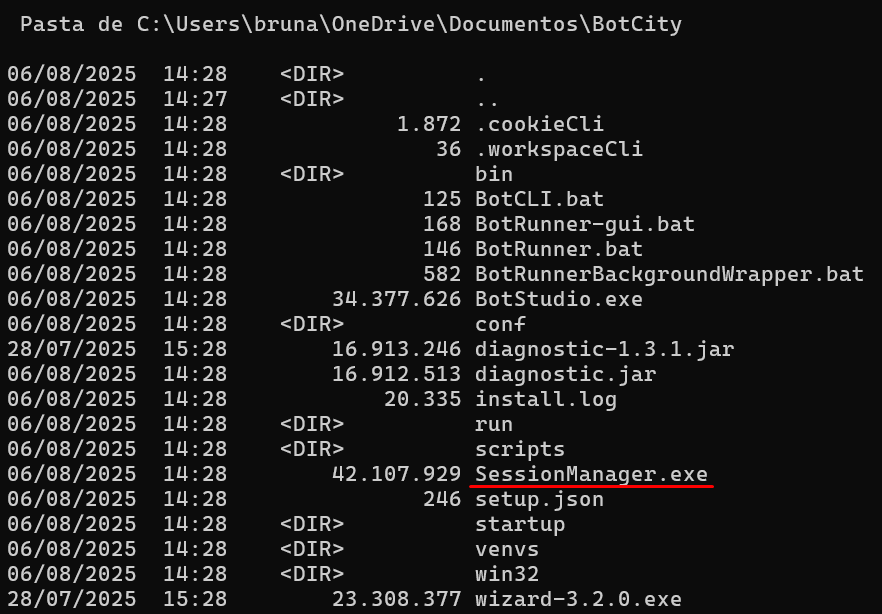
You should see the Session Manager executable listed, such as session-manager.exe or session-manager.
Step 3: Session Manager Configuration - Host¶
Configuration is done via terminal commands. The first command to use is to add a host:
In our context, we have two hosts, so let's add both, providing the following information:
-
First Host:
- Label for the host:
Remote-1 - Choose the protocol (rdp, ec2):
rdp - Username:
admin - Password:
Pass123 - Repeat for confirmation:
Pass123 - Hostname:
10.30.85.56 - Width:
1600 - Height:
900 - Port [3389]:
3389
- Label for the host:
-
Second Host:
- Label for the host:
Remote-2 - Choose the protocol (rdp, ec2):
rdp - Username:
administrator - Password:
123pass - Repeat for confirmation:
123pass - Hostname:
172.24.70.36 - Width:
1600 - Height:
900 - Port [3389]:
3389
- Label for the host:
Step 4: Session Manager Configuration - Runner¶
With the hosts added, the next step is to attach the Runners to each host.
Following the context:
Runner-Desktop-1,Runner-BG-1,Runner-BG-2toRemote-1Runner-Desktop-2,Runner-BG-3toRemote-2
To do this, use the command:
Fill in the information as per the context:
- Runner-Desktop-1:
- Host label:
Remote-1 - Runner label:
Runner-Desktop-1 - Path to SDK:
C:\Users\admin\BotCity\Runner-Desktop-1
- Host label:
- Runner-BG-1:
- Host label:
Remote-1 - Runner label:
Runner-BG-1 - Path to SDK:
C:\Users\admin\BotCity\Runner-BG-1
- Host label:
- Runner-BG-2:
- Host label:
Remote-1 - Runner label:
Runner-BG-2 - Path to SDK:
C:\Users\admin\BotCity\Runner-BG-2
- Host label:
- Runner-Desktop-2:
- Host label:
Remote-2 - Runner label:
Runner-Desktop-2 - Path to SDK:
C:\Users\administrator\BotCity\Runner-Desktop-2
- Host label:
- Runner-BG-3:
- Host label:
Remote-2 - Runner label:
Runner-BG-3 - Path to SDK:
C:\Users\administrator\BotCity\Runner-BG-3
- Host label:
Step 5: Configuration Verification¶
To check if the configuration was done correctly, use the command:
This command lists all hosts and associated Runners, allowing you to confirm if everything is as expected.
Step 6: Start Session Manager¶
With the configuration complete, the next step is to start Session Manager, so it can begin monitoring the BotCity Orchestrator task queue and managing the Runners.
To start Session Manager, use the command:
Monitor the sm_audit.log and sm_out.log logs in the log folder at the Session Manager installation location to check if everything is working correctly.
BotCity Orchestrator¶
Once Session Manager is running, it will start monitoring the BotCity Orchestrator task queue.
For proper operation, it is necessary that Automations in the Orchestrator are directed to the Runners attached to the hosts configured in Session Manager.
Automations¶
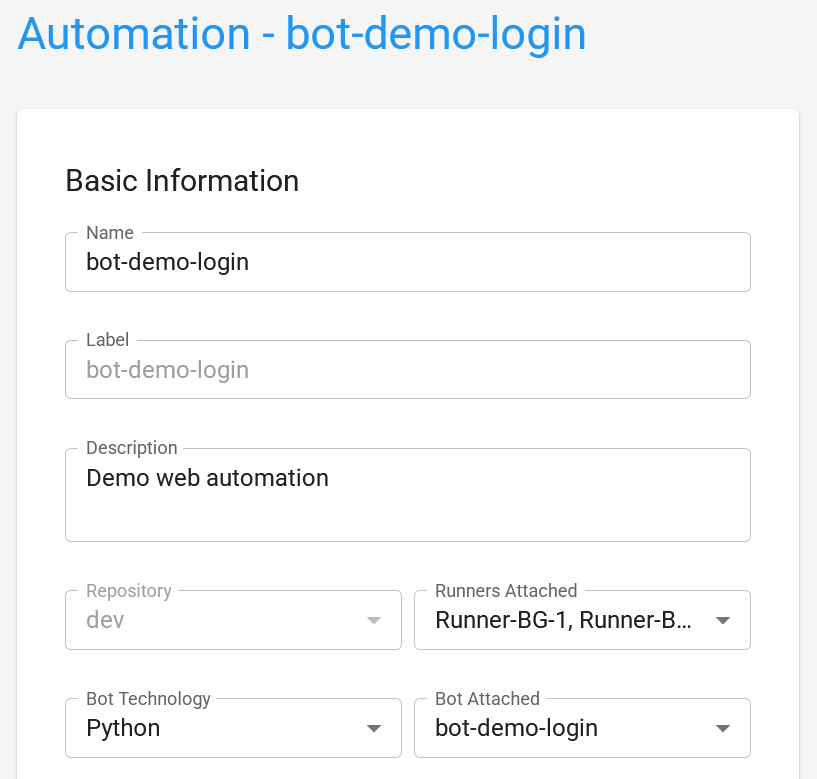
To check this, access BotCity Orchestrator, go to the Automations section, and select the desired automation.
In the Runners Attached field, one or more Runners attached in the Session Manager settings should be selected.
Tasks¶
At this point, when a new task is created, Session Manager will automatically access one of the configured hosts, start the attached Runner, and execute the automation.
When finished, and if there are no more tasks in the queue, Session Manager will disconnect from the host, freeing it for future executions.
Full Documentation¶
See the complete Session Manager documentation, accessing other functions and configurations at: Session Manager - BotCity Docs.